The Mediterranean Diet
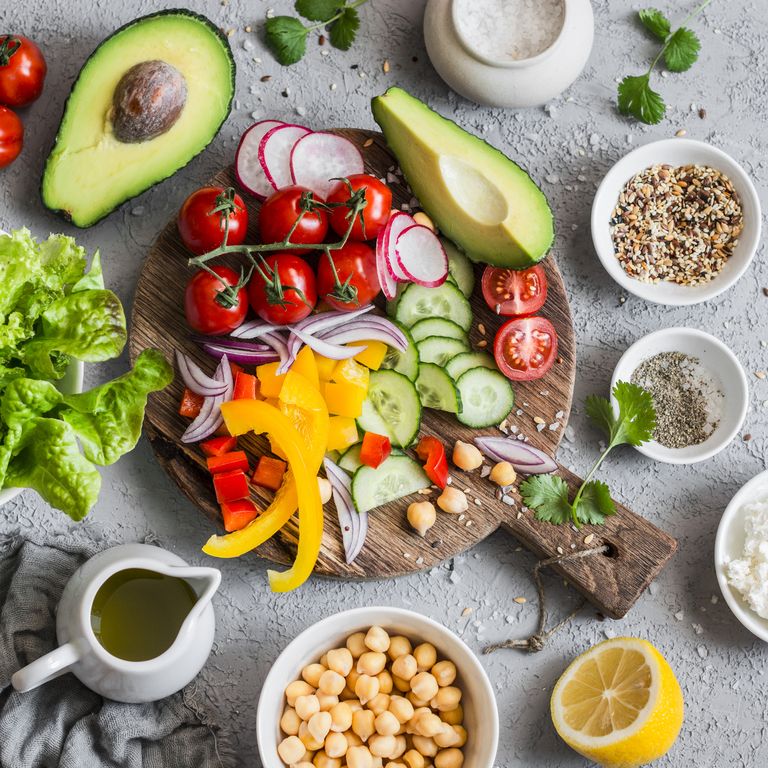
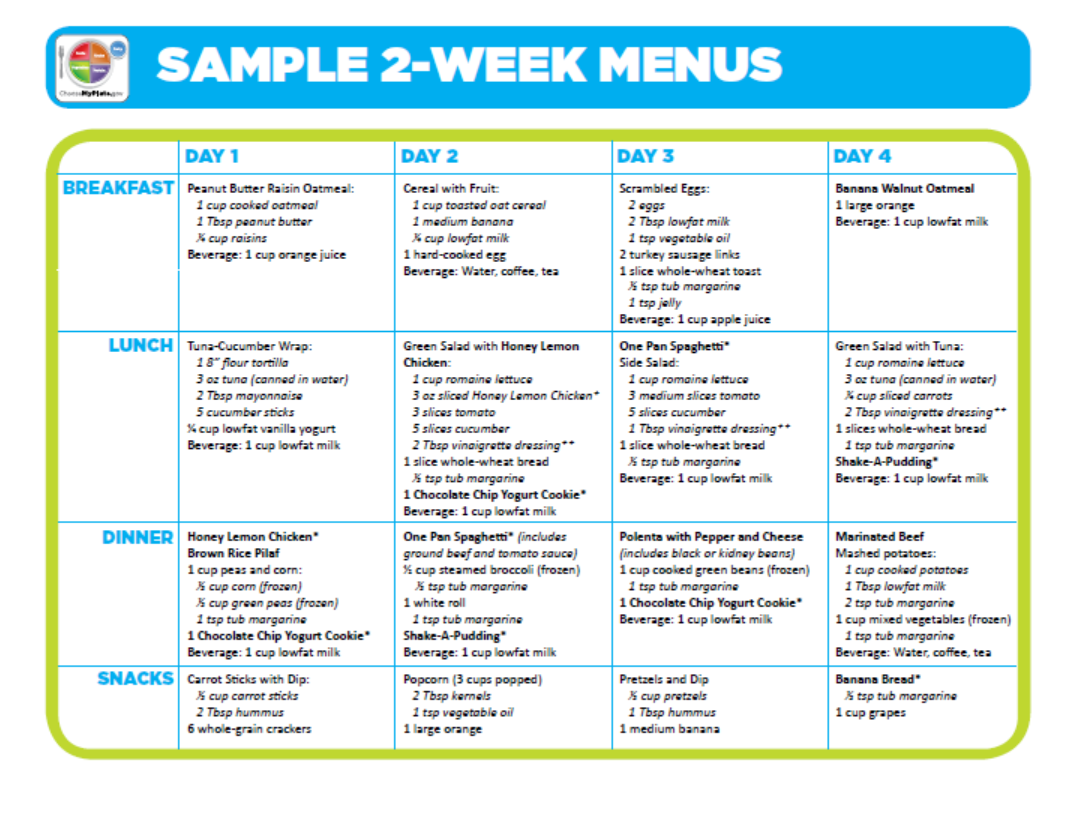
At GI for Kids, we sometimes encourage our patients to follow a Mediterranean Diet. This diet is high in fruits, vegetables, plant-based proteins, and healthy fats. A Mediterranean Diet can be prescribed for a specific condition, like constipation, or just as a general healthy diet.

A Mediterranean Diet includes many healthy foods. High fiber foods such as fruits, vegetables, beans, nuts/seeds may be helpful for constipation. Foods high in fiber also help you feel full more quickly This can make it easier to manage portion sizes. In addition, the many colors on a Mediterranean Diet plate may intrigue picky eaters.
Is a Mediterranean Diet Low in Fat?
Your doctor may recommend a “low fat diet” if you are diagnosed with fatty liver or elevated lipid levels. Although, not low in fat, a Mediterranean Diet may still be helpful for hyperlipidemia or fatty liver. While it is important to limit fat overall and restrict certain types of fats, we need fats in the diet. Fats aid in absorption of fat-soluble  vitamins, brain development, regulation of body temperature and protect our organs. In fact, 20-25% of our calories come from fat even on a “low fat diet” (up to a quarter of the calories you eat!).
vitamins, brain development, regulation of body temperature and protect our organs. In fact, 20-25% of our calories come from fat even on a “low fat diet” (up to a quarter of the calories you eat!).
Aside from limiting the amount of fat in the diet, it is also important to consider the types of fat you eat. If you are unfamiliar with the different types of fats in the diet you can read about them here. A Mediterranean Diet is high in unsaturated fats which can be helpful for your liver.
The types of carbohydrates included in a Mediterranean Diet may also be important for to your liver health. Carbohydrates, found in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and added sugars, are our main source of energy. Eating carbohydrates higher in fiber and lower in sugar helps our bodies to utilize this energy better. If we include too much added sugar in the diet, some of these carbohydrates may be stored as triglycerides (a type of fat) on the liver instead of being used for energy. Hint: exercise also helps us to use carbohydrates for energy!
Bottom Line
It is always best to consult with your doctor or dietitian before making significant changes in your diet. You can call our office to schedule and appointment with our dietitian, Madden, if you think the Mediterranean Diet may be appropriate for you!