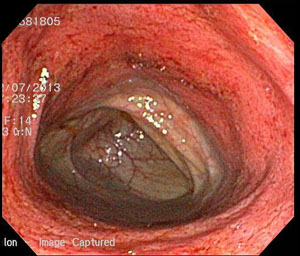
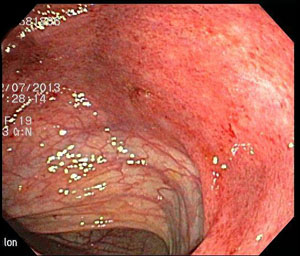
Ulcerative Colitis (UC) is a long-lasting (chronic) disease that causes inflammation and sores (ulcers) in the inner lining of the large intestine (colon) which includes the end part of the colon (rectum). It usually begins in the rectum and then spreads back into the colon. Ulcerative Colitis is one of two forms of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). The other form is called Crohn’s disease.
In UC, inflammation in the large intestine causes loss in the lining of the colon causing bleeding, pus, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. While this disease can be found in people of all ages, it usually develops between the ages of 15 and 30. The disease affects both men and women. It has been reported that approximately 500,000 to 2 million people in the United States have this disease. People with a close family member (brothers, sisters, parents) have an increased risk of getting this disease. UC can be found in all races—especially the white population and those of Jewish decent.
Cause
The cause of ulcerative colitis is not known but it likely involves the immune system working incorrectly to fight against harmful bacteria, viruses, fungi, and other invaders. When the immune system activates it causes inflammation in the tissues, and having inflammation for a long time (chronic) causes sores (ulceration).
Symptoms
The common symptoms of Ulcerative Colitis include rectal bleeding and diarrhea, but there is a wide range of symptoms and different types of UC depending on the location and the amount of inflammation:
- Ulcerative proctitis – inflammation is limited to the rectum. Mild bleeding every once in a while may be the only symptom. More severe symptoms include rectal pain, feeling of having to rush to the bathroom (urgency), and painful urge to go to the bathroom.
- Proctosigmoiditis – involves inflammation of the rectum and the short segment of the colon that goes to the rectum (sigmoid colon). Symptoms include rectal bleeding, urgency to go to the bathroom, and painful urge.
- Left-sided colitis – involves inflammation that starts at the rectum and extends up the left colon (sigmoid colon and the descending colon). Symptoms include bloody diarrhea, abdominal cramps, weight loss, and left-sided abdominal pain.
- Pancolitis or universal colitis – involves inflammation that affects the entire colon. Symptoms include bloody diarrhea, abdominal pain and cramps, weight loss, very tired (fatigued), fever, and night sweats.
- Fulminant colitis – is rare but severe. Symptoms include severe dehydration, abdominal pain, diarrhea with bleeding and even shock.
- Antibiotics (metronidazole)
- ASA anti-inflammatories (Azulfidine, Colazal, Asacol, Pentasa)
- Steroids (prednisone, prednisolone, budesonide)
- Immuno-modulators (Purinethol or Imuran)
- Biologicals (Remicade)
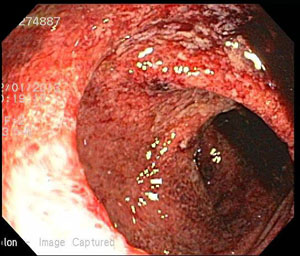
colitis – colon – sigmoid colon
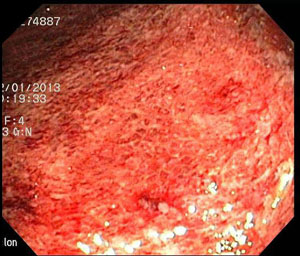
colitis – colon – decending colon
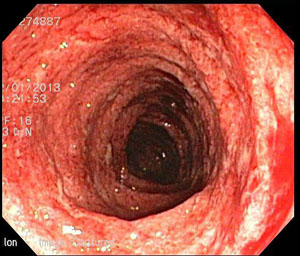
colitis-colon-transverse colon